- message passing model
- the Message Passing Interface (MPI) - standard interface
- MPI is only a definition for an interface
几个重要的概念
- communicator: 由一系列进程组成,拥有沟通的能力
- 每个进程都有 rank 沟通交流靠秩 + tag(标记信息)
-
point-to-point communications collective communications
编程篇
假设有个.c 文件 mpi
mpicc mpi_hello_world.c -o hello_world
mpirun -np 4 -f host_file hello_world //np 是processing的数量
//host_file 记录着集群的信息
host_file
Ailab1
Ailab2
Ailab3
如果不想平均分,想根据核数来 host_file
Ailab1:2
Ailab2:2
Ailab3:2
即可 有限Ailab1的两核,用完了再下一个
- Sending and receiving are the two foundational concepts of MPI.
- MPI allows senders and receivers to also specify message IDs with the message (known as tags)
send 和 recive 的原型
```c MPI_Send( void* data, int count, // 送出了这么多 exactly MPI_Datatype datatype, int destination, int tag, MPI_Comm communicator)
MPI_Recv( void* data, int count, // 最多接受这么多 at most MPI_Datatype datatype, int source, int tag, MPI_Comm communicator, MPI_Status* status)
##### mpi datatype
| MPI datatype | C equivalent
| ------------- |:-------------:
|MPI_SHORT |short int
|MPI_INT |int
|MPI_LONG |long int|
|MPI_LONG_LONG |long long int
|MPI_UNSIGNED_CHAR |unsigned char
|MPI_UNSIGNED_SHORT |unsigned short int
|MPI_UNSIGNED |unsigned int
|MPI_UNSIGNED_LONG |unsigned long int
|MPI_UNSIGNED_LONG_LONG |unsigned long long int
|MPI_FLOAT |float
|MPI_DOUBLE |double
|MPI_LONG_DOUBLE | long double
|MPI_BYTE |char
- 能够创建自己的own MPI datatypes
##### 动态传输
利用status
```c
MPI_Status status;
接收的长度
MPI_Get_count(&status, MPI_INT, &number_amount);
MPI_Probe(
int source,
int tag,
MPI_Comm comm,
MPI_Status* status)
像MPI_Recv 一样除了真实接收数据 动态接收数组
MPI_Probe(0, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
// When probe returns, the status object has the size and other
// attributes of the incoming message. Get the message size
MPI_Get_count(&status, MPI_INT, &number_amount);
// Allocate a buffer to hold the incoming numbers
int* number_buf = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * number_amount);
// Now receive the message with the allocated buffer
MPI_Recv(number_buf, number_amount, MPI_INT, 0, 0,
MPI_COMM_WORLD, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
- As an exercise, make a wrapper around MPI_Recv that uses MPI_Probe for any dynamic applications you might write. It makes the code look much nicer :-)
注意死锁的发生
- MPI_Send 要 receive 完之后才 return,如果大家都 send 那就死锁了,教程里解决死锁的办法是奇偶 rank 的执行顺序不同,奇的话是先收后发,偶的话是先发后收
MPI Broadcast and Collective Communication
- a synchronization point
- 用于同步的函数
MPI_Barrier(MPI_Comm communicator)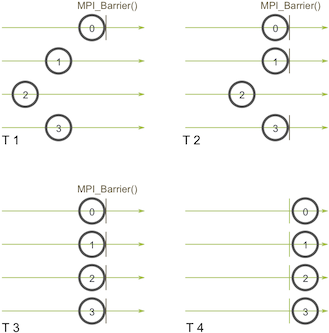
- broadcast: one process sends the same data to all processes in a communicator.
MPI_Bcast(
void* data,
int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype,
int root,
MPI_Comm communicator)
无论是 root 还是 receive 进程都需要调用MPI_Bcast 因为有变量指定了root broadcast utilizes a similar tree broadcast algorithm
MPI_Wtime(); // 返回时间戳
- MPI_Scatter 与 MPI_Bcast 很像, 唯一不同点是 MPI_Bcast 传相同数据而 MPI_Scatter 传不同的数据给不同的进程
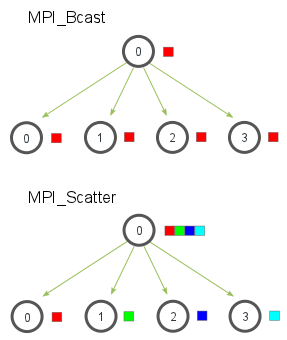
MPI_Scatter(
void* send_data,
int send_count,
MPI_Datatype send_datatype,
void* recv_data,
int recv_count,
MPI_Datatype recv_datatype,
int root,
MPI_Comm communicator)
- MPI_Gather
MPI_Gather( void* send_data, int send_count, MPI_Datatype send_datatype, void* recv_data, int recv_count, MPI_Datatype recv_datatype, int root, MPI_Comm communicator)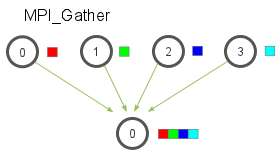
root 需要 receive buffer 其他的就传个 NULL 就可以
recv_count parameter 是每个进程发送的数量
- 参考代码 ```cpp if (world_rank == 0) { rand_nums = create_rand_nums(elements_per_proc * world_size); }
// Create a buffer that will hold a subset of the random numbers float *sub_rand_nums = malloc(sizeof(float) * elements_per_proc);
// Scatter the random numbers to all processes MPI_Scatter(rand_nums, elements_per_proc, MPI_FLOAT, sub_rand_nums, elements_per_proc, MPI_FLOAT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// Compute the average of your subset float sub_avg = compute_avg(sub_rand_nums, elements_per_proc); // Gather all partial averages down to the root process float *sub_avgs = NULL; if (world_rank == 0) { sub_avgs = malloc(sizeof(float) * world_size); } MPI_Gather(&sub_avg, 1, MPI_FLOAT, sub_avgs, 1, MPI_FLOAT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// Compute the total average of all numbers. if (world_rank == 0) { float avg = compute_avg(sub_avgs, world_size); }
- many-to-many communication pattern
- MPI_Allgather
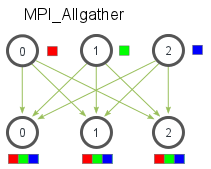
MPI_Allgather( void* send_data, int send_count, MPI_Datatype send_datatype, void* recv_data, int recv_count, MPI_Datatype recv_datatype, MPI_Comm communicator)
与上面相似的例程
// Gather all partial averages down to all the processes float *sub_avgs = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * world_size); MPI_Allgather(&sub_avg, 1, MPI_FLOAT, sub_avgs, 1, MPI_FLOAT, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// Compute the total average of all numbers. float avg = compute_avg(sub_avgs, world_size);
- 获取 mpi_datatype_size 的函数
```cpp
MPI_Type_size(datatype, &datatype_size); //the latter 是用来存储结果
- reduce 是缩小算法规模的意思
MPI_Reduce( void* send_data, void* recv_data, // 注意 recv_data 的大小是 sizeof(datatype) * count int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, int root, MPI_Comm communicator)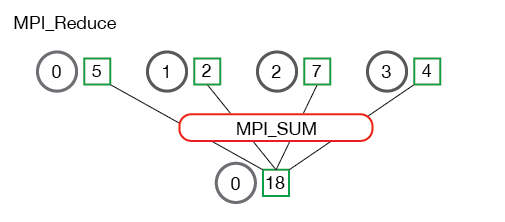 reduce operation 操作符
reduce operation 操作符 - MPI_MAX - Returns the maximum element.最大值
- MPI_MIN - Returns the minimum element.最小值
- MPI_SUM - Sums the elements.总和
- MPI_PROD - Multiplies all elements.累乘
- MPI_LAND - Performs a logical and across the elements.逻辑与
- MPI_LOR - Performs a logical or across the elements.逻辑或
- MPI_BAND - Performs a bitwise and across the bits of the elements.按位与
- MPI_BOR - Performs a bitwise or across the bits of the elements.按位或
- MPI_MAXLOC - Returns the maximum value and the rank of the process that owns it.最大值及进程的秩
-
MPI_MINLOC - Returns the minimum value and the rank of the process that owns it.最小值及进程的秩
- Allreduce 很明显 参数少了个 root
MPI_Allreduce( void* send_data, void* recv_data, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, MPI_Comm communicator)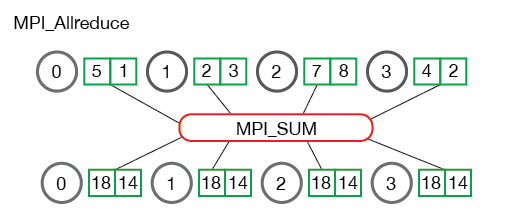
总结一下 到目前为止 common collectives 有
- MPI_Bcast,
- MPI_Scatter
- MPI_Gather
- MPI_Reduce
分割全局的通讯器COMMUNICATOR
就像下图一样
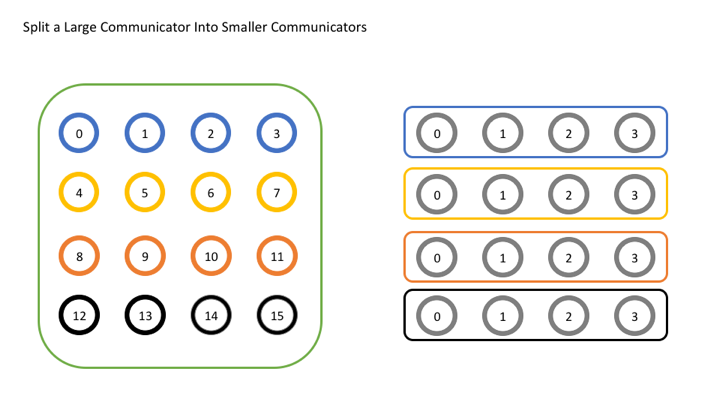 所需要的函数
所需要的函数
MPI_Comm_split(
MPI_Comm comm, //需要划分的communicator
int color, // 进程具有一样的 color 意味着是相同的 COMMUNICATOR
int key, // 这个值决定了进程在新的communicator里面的秩
MPI_Comm* newcomm) //返回的新的communicator
communicator 由ID 和 Group(set) 组成
MPI_Comm_group(
MPI_Comm comm,
MPI_Group* group)
求两个组的并集
MPI_Group_union(
MPI_Group group1,
MPI_Group group2,
MPI_Group* newgroup)
求两个组的交集
MPI_Group_intersection(
MPI_Group group1,
MPI_Group group2,
MPI_Group* newgroup)'
根据 rank 数组来提取出 group
MPI_Group_incl(
MPI_Group group,
int n,
const int ranks[],
MPI_Group* newgroup)
根据 group 产生 communicator
MPI_Comm_create_group(
MPI_Comm comm,
MPI_Group group,
int tag,
MPI_Comm* newcomm)
下面是例程
// Create a new communicator based on the group
MPI_Comm prime_comm;
MPI_Comm_create_group(MPI_COMM_WORLD, prime_group, 0, &prime_comm);
int prime_rank = -1, prime_size = -1;
// If this rank isn't in the new communicator, it will be
// MPI_COMM_NULL. Using MPI_COMM_NULL for MPI_Comm_rank or
// MPI_Comm_size is erroneous
if (MPI_COMM_NULL != prime_comm) {
MPI_Comm_rank(prime_comm, &prime_rank);
MPI_Comm_size(prime_comm, &prime_size);
}
判断 MPI_COMM_NULL 很重要 区分是否是是新 communicator 中的一员